In Texas, buck antler restrictions are designed to promote the sustainable management of deer populations. The intent of this harvest regulations is to improve the age structure of bucks within the herd. The Texas deer hunting antler restrictions apply in specific counties and aim to protect younger bucks, encouraging the harvest of older deer.
In almost all cases, antler restriction regulations exist in counties that have very high deer hunting pressure. Fortunately, antler restrictions allow harvest opportunities while protecting and sustaining some of the buck segment of the deer herd. In fact, without antler restrictions in place in certain counties, yearling bucks (1 1/2 years of age) would comprise almost all of the buck harvest annually.

Overview of Texas Deer Hunting Antler Restrictions
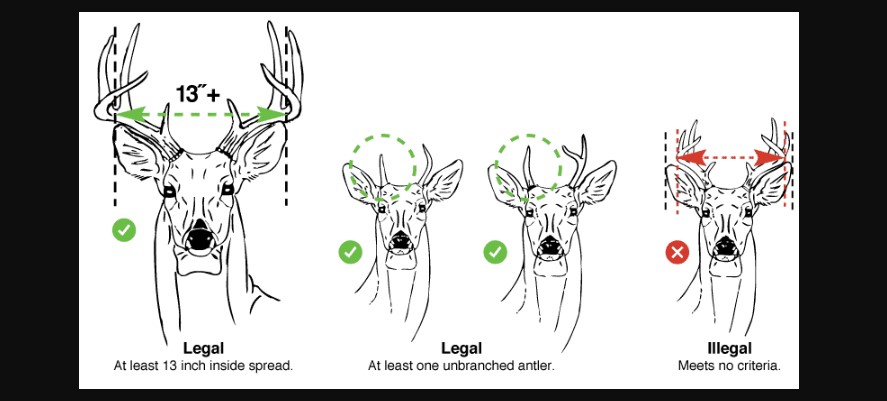
A buck is considered legal in restricted counties if it has at least one unbranched antler or an inside spread of 13 inches or greater between the main beams. This approach helps maintain a balanced age structure in deer populations. In turn, this supports healthy deer populations and reproduction. These regulations also providing hunters with opportunities to harvest older and better bucks. Understanding and following these restrictions is essential for ethical hunting and deer management efforts in certain counties across the state.
Texas deer hunting regulations include specific antler restrictions to help manage deer populations and improve herd quality. These Texas deer hunting antler restrictions help ensure better herds into the future. Here are the detailed guidelines regarding antler restrictions in Texas:
General Antler Restrictions
In certain Texas counties, antler restrictions apply to buck deer to encourage the harvest of older deer and prevent overharvesting of younger bucks.
Antler restrictions make only two types of bucks legal. These are defined as follows:
- A buck must have at least one unbranched antler (also called a “spike”), OR
- A buck must have an inside spread between the main beams of 13 inches or greater.
- A hunter can harvest up to two bucks in an antler restriction county.
- A hunter can harvest up to two bucks with at least one unbranched antlers in an antler restriction county.
- Hunters can shoot only one buck with an inside spread equal to or greater than 13 inches in an antler restriction county.

How to Measure the Inside Spread of the Main Beams
- Measure the inside spread at the widest point between the main beams.
- The spread must be 13 inches or more to meet the legal requirement in antler restricted counties.
Important Notes
- Hunters are allowed to harvest no more than two bucks per year in counties with antler restrictions. Use this link to see if antler restrictions exist in the county you hunt.
- Of these two bucks, only one may have an inside spread of 13 inches or greater.
Counties with Texas Deer Hunting Antler Restrictions
- Not all Texas counties have antler restrictions.
- The Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (TPWD) website provides a list of counties where these restrictions are enforced. It is important to consult the TPWD Outdoor Annual Hunting Regulations or your local county’s hunting regulations to confirm.
Exceptions to Antler Restrictions
- Antlerless deer (does) may be harvested during specific seasons or with special permits, depending on the county.
- Some counties have Youth-Only hunting seasons where antler restrictions may not apply for certain young hunters. Check TPWD regulations for details.
Purpose of Antler Restrictions
- Encourage hunters to target older, more mature bucks.
- Improve the overall health and genetic quality of deer herds.
- Ensure sustainable deer populations for future generations.
For the most accurate and up-to-date information, visit the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (TPWD) website or consult the TPWD Outdoor Annual Hunting Regulations.
Review of Texas Deer Hunting Antler Restrictions
Managing for a balanced age structure in whitetail deer bucks is crucial for maintaining a healthy deer herd. A balanced age structure ensures that deer populations remain stable, with enough mature bucks to breed within a confined period. It’s also important to have a mix of younger and older bucks to support natural population dynamics.
This balance promotes genetic diversity, which is vital for the overall health and resilience of the herd. Additionally, having a range of age classes helps ensure a more defined breeding period with some level of buck harvest. Removing some bucks and does keeps the herd stable. Allowing the population to grow unchecked can lead to habitat degradation, food scarcity, and increased disease transmission. By encouraging the harvest of deer in a way that maintains age diversity, wildlife managers can enhance the quality of hunting experiences and contribute to the long-term conservation of deer and their habitats.
Antler restrictions are not perfect, but Texas’ deer hunting antler restrictions do allow for a healthy deer population while allowing for the harvest of slightly older bucks. Like too little deer harvest, too much hunting pressure is a bad thing from a deer management and population standpoint. Hopefully, this article provided you with more context on why antler restrictions are part of the deer hunting season in some counties in Texas.